

So for question one, the first question that is option D. As mentioned several times, the expected value is the sum of the outcomes xi weighted by. As Hays notes, the idea of the expectation of a random. Where p() is some function returning the probability of the outcome. (keep in mind that the variance of the estimate -x-bar- is just scaled by the sample size, n).
#EXPECTED VALUE OF XBAR PDF#
Hint: Use the normal pdf and obtain the 2nd and 4th moments for X and then use the definition of variance. So the answer to our question is actually the population mean mu there's option D. The expected value of a random variable is the arithmetic mean of that variable. I want to calculate variance of X-bar2, (mean of X)2, when Xi Normal(theta, sigma2) and sigma is known. So and it has a formula if it's a discrete property distribution, it has a formula of X times P of X, and if it's a continuous distribution, it is the integral of X times F of X. So where we have a sample distribution on the expected value is also known as the population mean. The expected value of the random variable the sample mean exhibit is actually across towards. Step 2: Enter all values numerically and separate them by commas. If the population has a normal distribution, the sampling distribution of x is a normal distribution. So the first question is are the expected value of the random variable? Excuse me, the expert. Step 1: Enter all known values of Probability of x P (x) and Value of x in blank shaded boxes. The form of the sampling distribution of the sample mean depends on the form of the population. the value calculated using the distributions equation for variance.

Variance is defined as expected value of squared deviations from the mean 1.
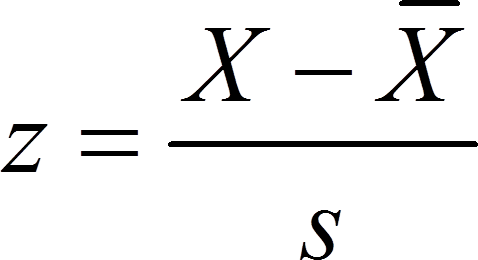
To calculate standard deviation we first need the variance. Given a sample of n observations of numbers, the sample mean is found by adding up all of the observations, then dividing by the total number of. Answer (1 of 7): Because if we didn’t square it we would always calculate it as zero. So we have two questions right here, we have question 25. In probability theory and statistics, variance is the expectation of the squared deviation of a random variable from its population mean or sample mean. X-bar in statistics is a symbol for the sample mean. The expected value of the random variable the sample mean (X bar) is the standard error the population standard deviation (0) the size of the population the.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
